- GK Home
-
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system -
Muscular System
-
Skeletal System
-
Nervous System
-
Reproductive System
-
Cardiovascular system
-
 Embedded system
Embedded system -
Genetics
-
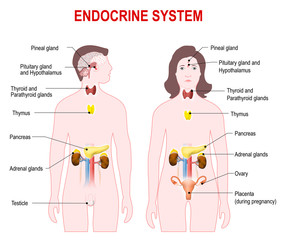 Endocrine system
Endocrine system -
Respiratory system
-
Urinary system
-
 জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন -
 কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি -
 মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি -
 বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ -
 উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ -
 প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
Organ System Reproductive System
⚠ Report Question ✓ Question Verified
Q: Which of the following hormones is not secreted from the corpus luteum?
Learn More MCQ Questions from Organ System Reproductive System
This set of MCQs tests your knowledge of the reproductive system, including the male and female reproductive systems, gametogenesis, fertilization, pregnancy, menstrual cycle, and hormone regulation. Test yourself with these multiple-choice questions and improve your understanding of reproductive biology.