Analyze Site Structure on SEO
Before seeing this ,if you don’t have any idea about SEO then you may have to look our previous post – SEO Introduction and
#1. SEO Basic
Or if you know something about SEO go forward.
#1. Improve the structure of your URLs
Simple-to-understand URLs will contain content information easily
Creating descriptive categories and filenames for the documents on your website can not only help you keep your site better organized, but it could also lead to better crawling of your documents by search engines. Also, it can create easier, "friendlier" URLs for those that want to link to your content. Visitors may be intimidated by extremely long and cryptic URLs that contain few recognizable words.
URLs like –https://www.example.com/floder1/12524/67849/7689bas.html
can be confusing and unfriendly. The user can not understand easily what this page for.
URLs like – https://www.example.com/blog/seo-techniques.html
can be easily understood by user what this page for. This page clearly shows that it contains information about SEO.
URLs are displayed in search results
Remember that the URL of a document is displayed as part of a search result in Google, below the document's title and snippet. Like the title and snippet, words in the URL on the search result appear in bold if they appear in the user's query.
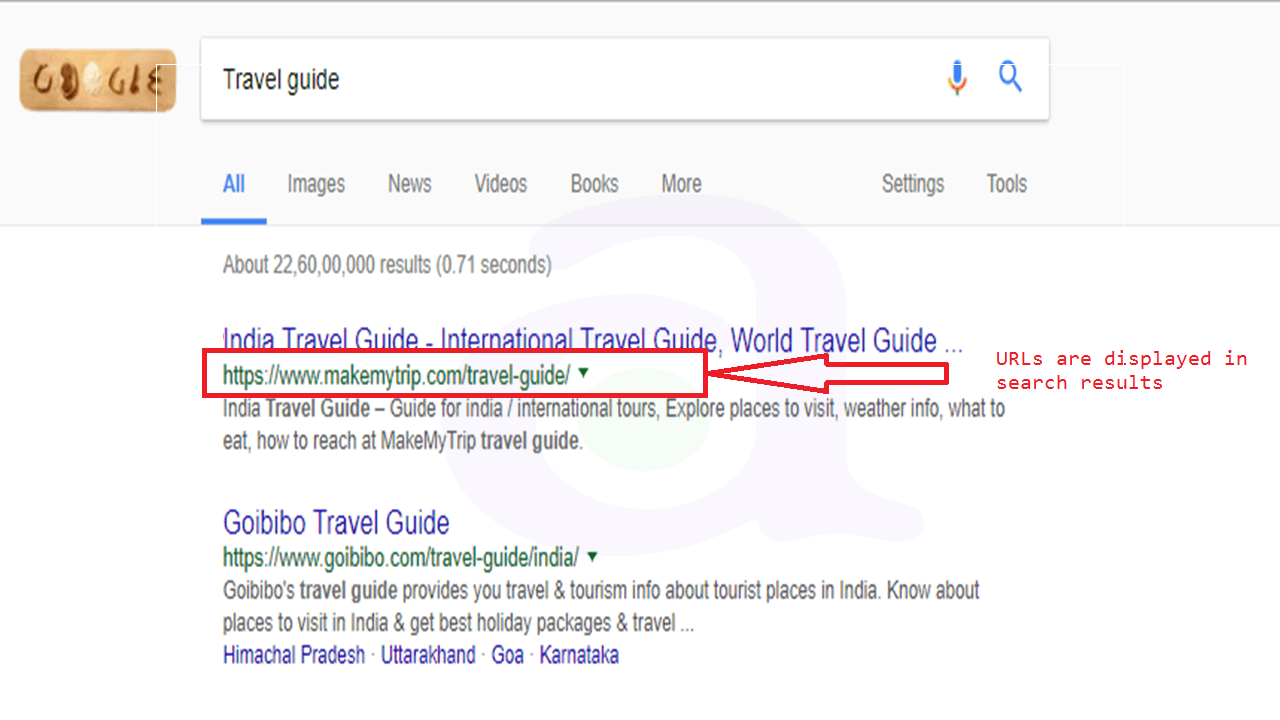
Google is good at crawling all types of URL structures, even if they're quite complex, but spending the time to make your URLs as simple as possible for both users and search engines can help. Some webmasters try to achieve this by rewriting their dynamic URLs to static ones; while Google is fine with this, we'd like to note that this is an advanced procedure and if done incorrectly, could cause crawling issues with your site. To learn even more about good URL structure, we recommend this Webmaster Help Center page on creating Google-friendly URLs.
DO:
1. Use readable URLs: URLs with words that are relevant to your site's content and structure are friendlier for visitors navigating your site. Use target keyword with your URL, so that Visitors remember them better and might be more willing to link to them.
2. Create a simple directory structure: Use a directory structure that organizes your content well and makes it easy for visitors to know where they're at on your site
3. Use 301 redirect: Tell Google about changes to your URLs, so you don’t lose your ranking.
4. Use canonical URL: Avoid a duplicate content penalty by telling search engines your preferred domain and preferred webpages.
5. Add Mobile URLs to sitemaps: Identify mobile friendly pages in sitemaps so they get ranked higher in mobile search results.
6. Always use hyphens in URLs:Google does not read underscore. So be careful about that.
DON'T:
1. Using lengthy URLs with unnecessary parameters and session IDs
2. Choosing generic page names like "page1.html".
3. Using excessive keywords like "travel-guide-travel-guide-travelguide.html"
4. Having deep nesting of subdirectories like ".../dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/dir5/dir6/page.html"
5. Using directory names that have no relation to the content in them.
6. Having pages from subdomains and the root directory access the same content.
e.g. "example.com/page.html" and "sub.example.com/page.html"
7. Using odd capitalization of URLs - many users expect lower-case URLs and remember them better.
8. Using underscore in URLs
#2. Make your site easier to navigate:
Navigation is very important for search engines
The navigation of a website is important in helping visitors quickly find the content they want. It can also help search engines understand what content the webmaster thinks is important. Although Google's search results are provided at a page level, Google also likes to have a sense of what role a page plays in the bigger picture of the site.
Plan out your navigation based on your homepage
All sites have a home or "root" page, which is usually the most frequented page on the site and the starting place of navigation for many visitors. Unless your site has only a handful of pages, you should think about how visitors will go from a general page (your root page) to a page containing more specific content.
Ensure more convenience for users by using ‘breadcrumb’ lists
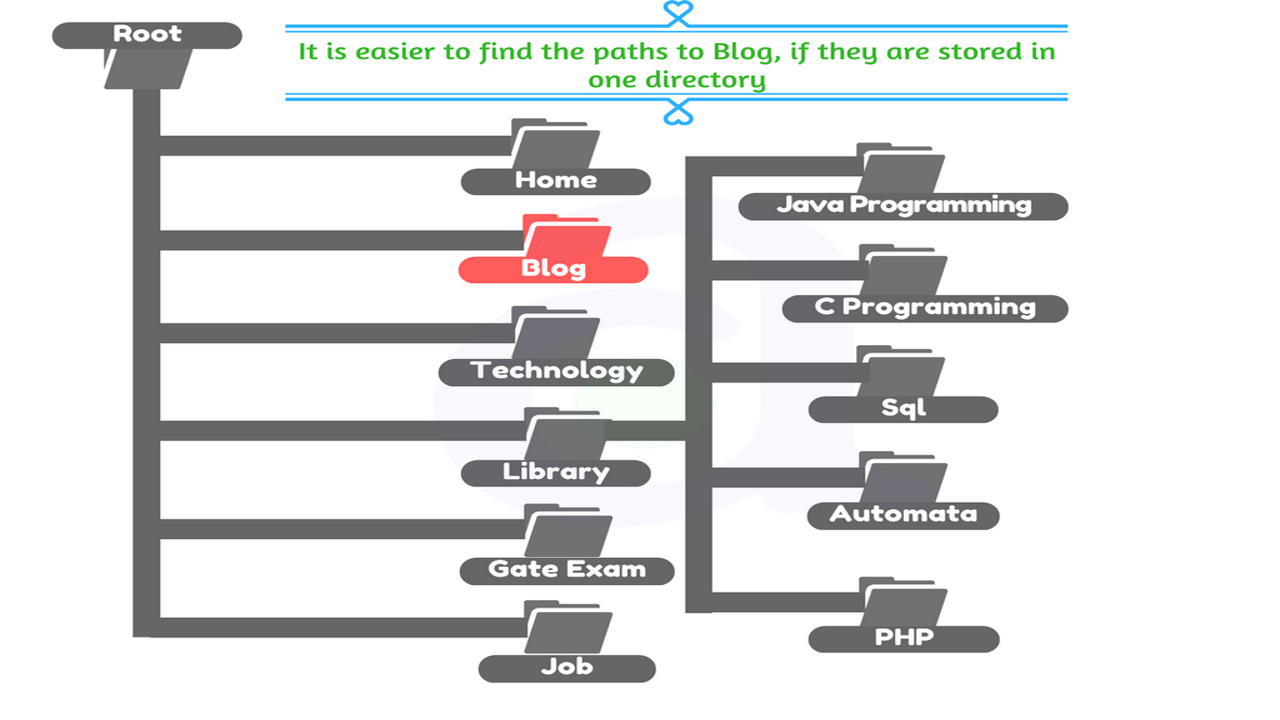
A ‘breadcrumb’ is a row of internal links at the top or bottom of the page that allows visitors to quickly navigate back to a previous section or the root page.
Allow for the possibility of a part of the URL being removed
Consider what happens when a user removes part of your URL - Some users might navigate your site in odd ways, and you should anticipate this. For example, instead of using the ‘breadcrumb’ links on the page, a user might drop off a part of the URL in the hopes of finding more general content. He or she might be visiting "http://www.example.com/india/2010/upcoming-movie-list.html" but then enter "http://www.example.com/india/2010/" , into the browser's address bar, believing that this will show all indian movies from 2010. Is your site prepared to show content in this situation or will it give the user a 404 error ("page not found" error)?
Prepare two sitemaps: one for users, one for search engines
A sitemap (lower-case) is a simple page on your site that displays the structure of your website and usually consists of a hierarchical listing of the pages on your site. Visitors may visit this page if they are having problems finding pages on your site. While search engines will also visit this page, getting good crawl coverage of the pages on your site, it's mainly aimed at human visitors.
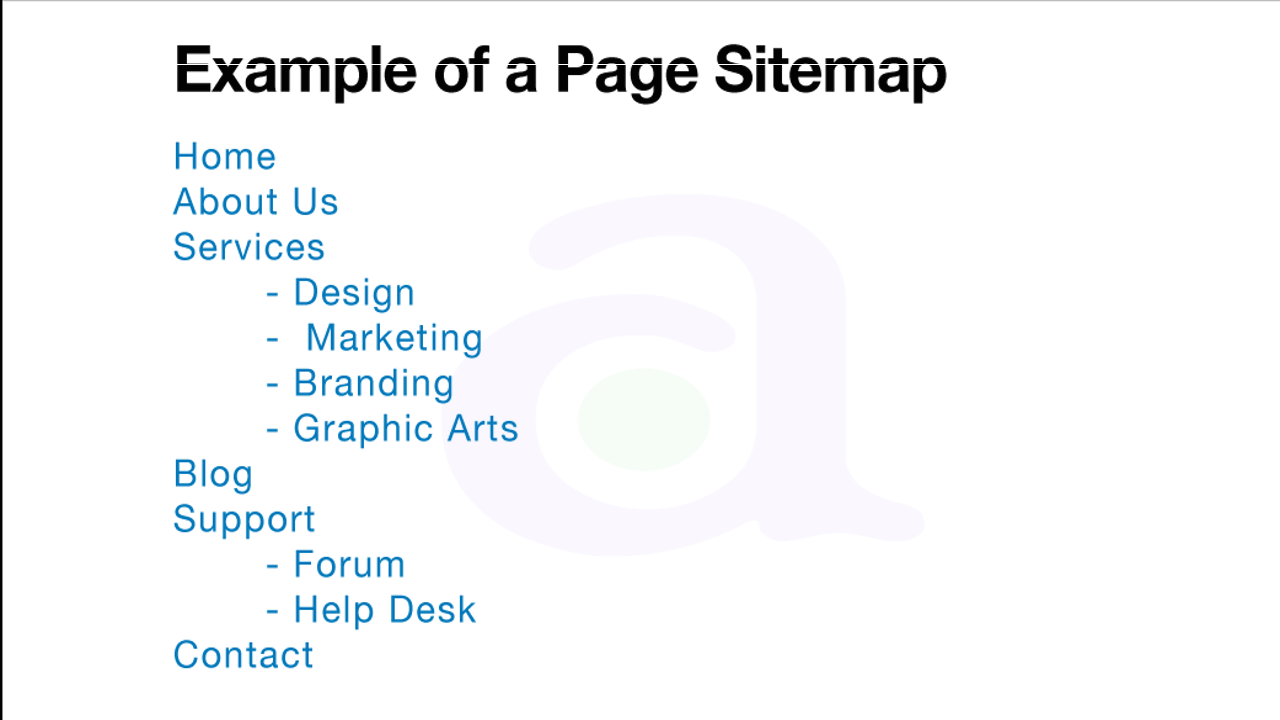
An XML Sitemap (upper-case) file, which you can submit through Google's Webmaster Tools, makes it easier for Google to discover the pages on your site. Using a Sitemap file is also one way (though not guaranteed) to tell Google which version of a URL you'd prefer as the canonical one (e.g. "http://exmple.com/" or "http://www.exmple.com/"; more on what's a preferred domain). Google helped create the open source Sitemap Generator Script to help you create a Sitemap file for your site. To learn more about Sitemaps, the Webmaster Help Center provides a useful guide to Sitemap files.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"> <url> <loc>http://www.exmple.com/</loc> <changefreq>daily</changefreq> <priority>0.8</priority> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.exmple.com/india/</loc> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.exmple.com/india/2008/</loc> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.exmple.com/india/2009/</loc> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.exmple.com/india/2010/</loc> </url> </urlset>
"For navigation, the focus should be on simplicity and ease of use! "
DO:
1. Make it as easy as possible for users to go from general content to the more specific content they want on your site. Add navigation pages when it makes sense and effectively works these into your internal link structure.
2. Controlling most of the navigation from page to page on your site through text links makes it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your site. Many users also prefer this over other approaches, especially on some devices that might not handle Flash or JavaScript.
3. A simple site map page with links to all of the pages or the most important pages (if you have hundreds or thousands) on your site can be useful. Creating an XML Sitemap file for your site helps ensure that search engines discover the pages on your site.
4. Users will occasionally come to a page that doesn't exist on your site, either by following a broken link or typing in the wrong URL. Having a custom 404 page that kindly guides users back to a working page on your site can greatly improve a user's experience. Your 404 page should probably have a link back to your root page and could also provide links to popular or related content on your site. Google provides a 404 widget that you can embed in your 404 page to automatically populate it with many useful features. You can also use Google Webmaster Tools to find the sources of URLs causing "not found" errors.
DON'T:
1. Creating complex webs of navigation links, e.g. linking every page on your site to every other page
2. Going overboard with slicing and dicing your content (so that it takes twenty clicks)
3. Having a navigation based entirely on drop-down menus, images, or animations - many, but not all, search engines can discover such links on a site, but if a user can reach all pages on a site via normal text links, this will improve the accessibility of your site; more on how Google deals with non-text files.
4. Letting your HTML site map page become out of date with broken links.
5.Creating an HTML sitemap that simply lists pages without organizing them, for example by subject.
6. Allowing your 404 pages to be indexed in search engines (make sure that your webserver is configured to give a 404 HTTP status code when non-existent pages are requested).
7. Providing only a vague message like "Not found", "404", or no 404 page at all.
8. Using a design for your 404 pages that isn't consistent with the rest of your site.
#3. Make effective use of robots.txt
robots.txt:
Robots.txt file is basically a text file which contain some instruction for web-crawlers. As a example Googlebot is web-crawling robot for Google and Bingbot is a web-crawling robot for Bing.
This robots are collects documents from the web to build a searchable index for the Google and Bing.
Here the role of robots.txtfile is to prevent crawl those parts (files or pages) of your site which you don’t want accessed by search engine crawlers.
Note: You should not use robots.txtas a means to hide your important web pages from Google Search results.
This is because other pages might point to(linked to) your page, and your page could get indexed that way, avoiding the robots.txtfile. If you want to block your page from search results, use another method such as password protection or noindex tags.
Then, what are the use of robots.txtfile??
robots.txtshould only be used to control crawling traffic, If Googlebot crawl that type of pages which is not related to user or created for testing purpose only then your server will be overwhelmed by Google's crawler that means wasted of crawl budget.
Also, robots.txtdoes prevent image files from appearing in Google search results. But it does not prevent other pages or users from linking to your image.
However, it is not good idea to block that type of file (style, script) or image which is needed to understand your useful web-page.
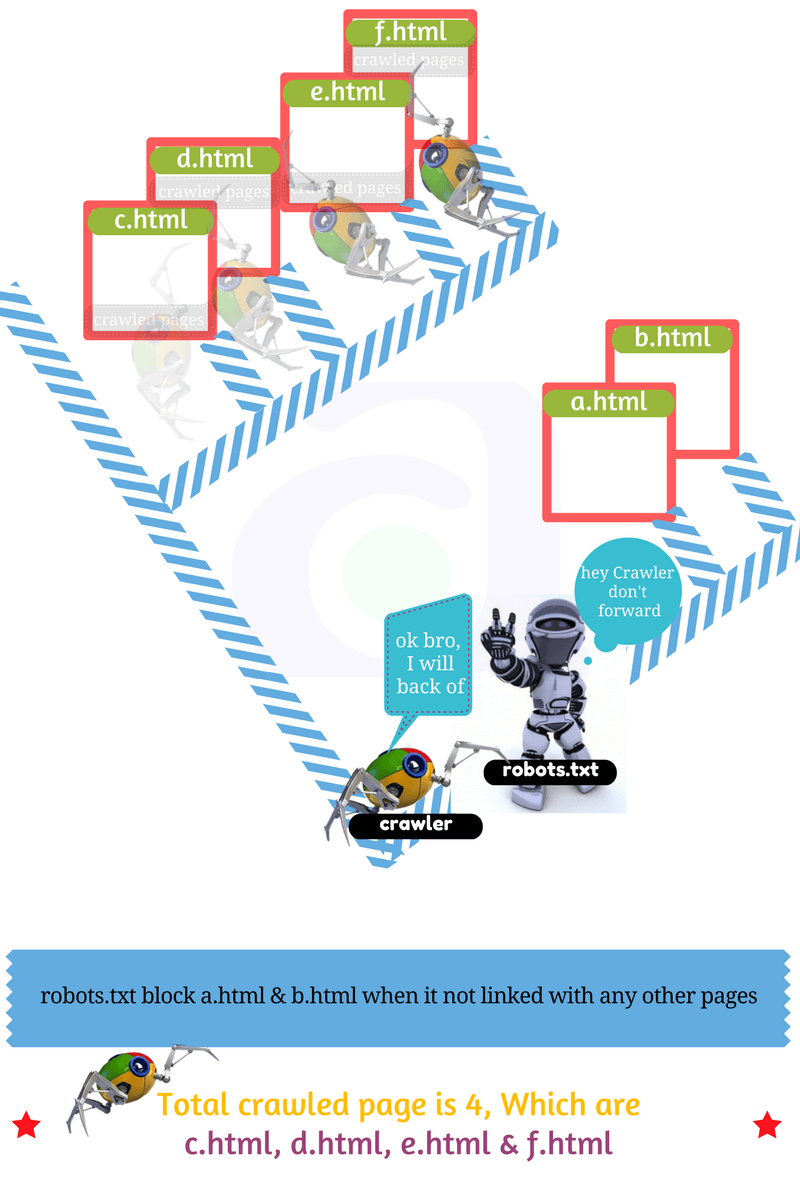
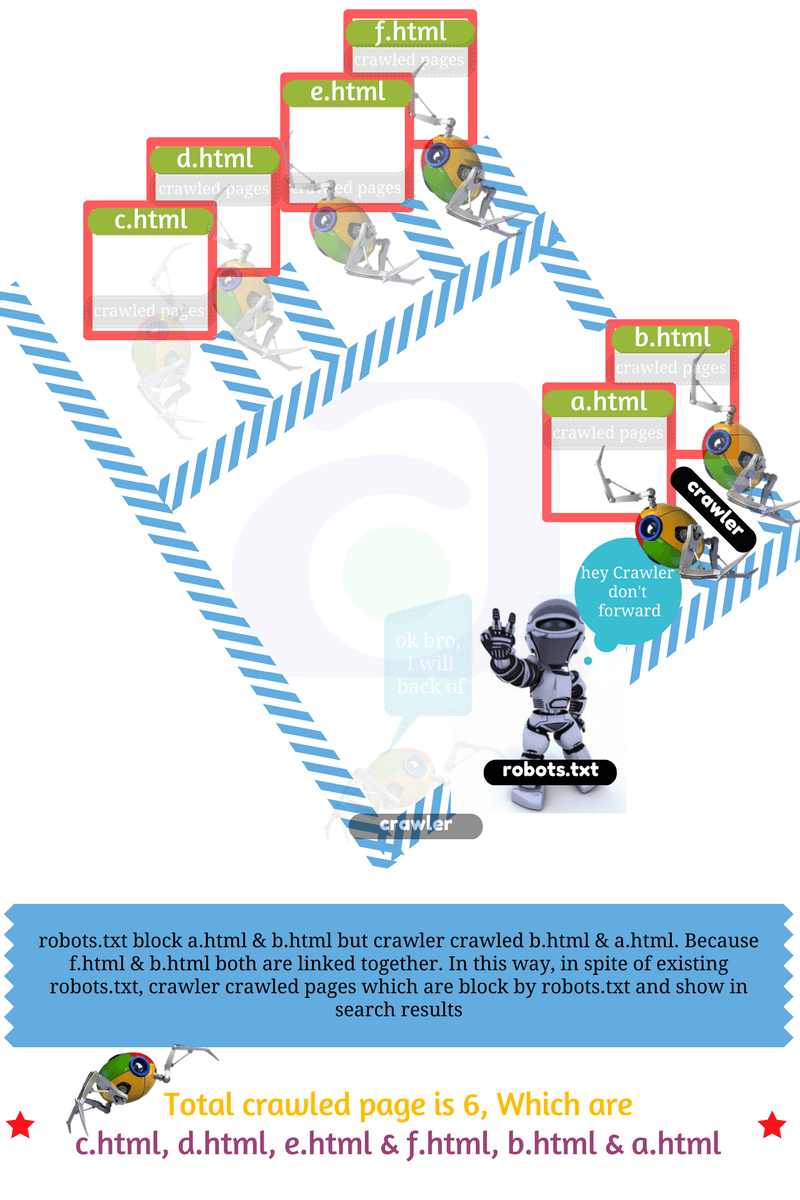
Limitations of robots.txt:
Before you build your robots.txt, you should know the risks of this URL blocking method. At times, you might want to consider other mechanisms to ensure your URLs are not findable on the web.
#1. The instructions in robots.txtfiles cannot enforce crawler behavior to your site; instead, these instructions act as directives to the crawlers accessing your site. While Googlebot and other respectable web crawlers obey the instructions in a robots.txtfile, other crawlers might not. Therefore, if you want to keep information secure from web crawlers, it’s better to use other blocking methods, such as password-protecting private files on your server.
#2. Although respectable web crawlers follow the directives in a robots.txtfile, each crawler might interpret the directives differently. You should know the proper syntax for addressing different web crawlers as some might not understand certain instructions.
#3. While Google won't crawl or index the content blocked by robots.txt, we might still find and index a disallowed URL from other places on the web. As a result, the URL address and, potentially, other publicly available information such as anchor text in links to the site can still appear in Google search results. You can stop your URL from appearing in Google Search results completely by using other URL blocking methods, such as password-protecting the files on your server or using the noindex meta tag or response header.
If a robot wants to visit a Web site URL, say "http://www.example.com/welcome.html". Before it does so, it firsts checks for "http://www.example.com/robots.txt", and finds:
//robots.txt says..never visit any of the page of this site User-agent: * Disallow: /
The "User-agent: *" means this section applies to all robots. If it only for google search engine then replace * to Googlebot The "Disallow: /" tells the robot that it should not visit any pages on the site.
//robots.txt says..visit all the page of this site User-agent: * Disallow:
This example gives full permission to crawl all the pages of this site.
//robots.txt says never visit folder a & b. User-agent: * Disallow: /a/ Disallow: /b/
This example shows that robots should not visit file a, and file b. Now, I think you can create your own robots.txtfile as your requirement.
Put robots.txtfile into the root folder
Lets talk about "noindex" meta tag,
The robots meta tag lets you utilize a granular, page-specific approach to controlling how an individual page should be indexed and served to users in search results. Place the robots meta tag in the <head> section of a given page, like this:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head> <meta name="robots" content="noindex" /> (…) </head> <body>(…)</body> </html>
The robots meta tag in the above example instructs all search engines not to show this page in search results.
The value of the name="robots" indicates to all crawler.
If you want to block this page for specific robot then you have to change the value of name attribute. Only to block for Google search engine you have to put the value of name attribute is Googlebot and to block for Bing search engine put Bingbot.
If you put the value Googlebot then it will only work for Google Search Engine not for others.
Search Engine may have different crawlers for different search purpose. Let’s see the list of Google Search Crawlers.
Now, content="noindex" tells web-crawlers that do not show this page in search results.
If you put content="nofollow", that means search engine will not follow the link which is given in this page.
You can create multi-directive instruction by combining meta tag directives with comma.
As a example:
<head> <title></title> <meta name="robot" content="noindex, nofollow"> </head>
Let’s see the password protection directory of your server to protect URL:
If you have some confidential or private file which you don’t want to appear with search result, the simplest and most effective way to block private URLs from appearing is to store them in a password-protected directory on your site server. Googlebot and all other web crawlers are unable to access content in password-protected directories.
Now let’s see..
#5. Link Building