- GK Home
-
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system -
Muscular System
-
Skeletal System
-
Nervous System
-
Reproductive System
-
Cardiovascular system
-
 Embedded system
Embedded system -
Genetics
-
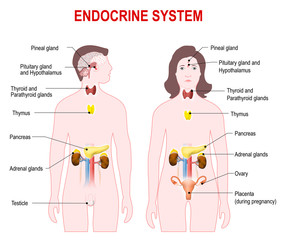 Endocrine system
Endocrine system
-
Respiratory system
-
Urinary system
-
 জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন -
 কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি -
 মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি -
 বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ -
 উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ -
 প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
⚠ Report Question ✓ Question Verified
Q: Which of the following hormones is classified as fat soluble?
Learn More MCQ Questions from Organ System Endocrine system
Here we learn about endocrine system of the organ system related to biology section and it comes under zoology. Share we can gain knowledge about endocrine system by analysing more MCQs related to it.