- GK Home
-
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system -
Muscular System
-
Skeletal System
-
Nervous System
-
Reproductive System
-
Cardiovascular system
-
 Embedded system
Embedded system -
Genetics
-
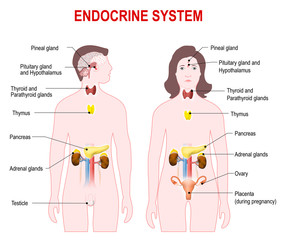 Endocrine system
Endocrine system -
Respiratory system
-
Urinary system
-
 জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন -
 কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি -
 মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি -
 বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ -
 উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ -
 প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
Organ System Cardiovascular system
⚠ Report Question ✓ Question Verified
Q: What is the primary function of blood platelets?
Learn More MCQ Questions from Organ System Cardiovascular system
Here, let us know about cardiovascular system of our body by analysing many McQs with explanations and get a knowledge from that.