- GK Home
-
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system -
Muscular System
-
Skeletal System
-
Nervous System
-
Reproductive System
-
Cardiovascular system
-
 Embedded system
Embedded system -
Genetics
-
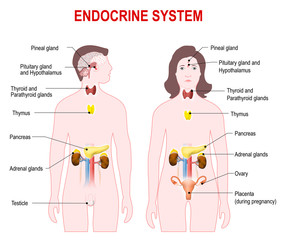 Endocrine system
Endocrine system -
Respiratory system
-
Urinary system
-
 জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন -
 কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি -
 মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি -
 বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ -
 উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ -
 প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
⚠ Report Question ✓ Question Verified
Q: What restores the resting potential after a nerve impulse?
Learn More MCQ Questions from Organ System Nervous System
This set of MCQs tests your knowledge of the nervous system, including neurons, action potential, synapses, neurotransmitters, brain, spinal cord, sensory receptors, and motor neurons. Test yourself with these multiple-choice questions and improve your understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system.