- GK Home
-
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system -
Muscular System
-
Skeletal System
-
Nervous System
-
Reproductive System
-
Cardiovascular system
-
 Embedded system
Embedded system -
Genetics
-
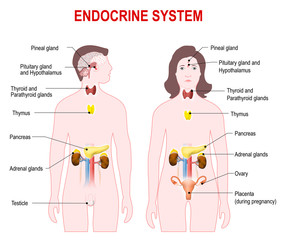 Endocrine system
Endocrine system -
Respiratory system
-
Urinary system
-
 জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন -
 কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি -
 মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি -
 বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ -
 উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ -
 প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
⚠ Report Question ✓ Question Verified
Q: Which of the following potentials does acetylcholine generate in the sarcolemma?
Learn More MCQ Questions from Organ System Muscular System
The muscular system is responsible for movement and stability in the human body. Learn about its anatomy, function, and common conditions with our comprehensive guide.